What is unified threat management (UTM)?
Unified threat management (UTM) is an information security system that provides a single point of protection against cyberthreats, including viruses, worms, spyware and other malware, as well as network attacks. It unifies cybersecurity, performance, management and compliance capabilities so administrators can manage network security from one system.
Unlike antivirus tools, UTM systems don't just protect PCs and servers against advanced threats, such as phishing attacks. These systems scan all network traffic, filtering potentially dangerous content and blocking intrusions to protect the entire network, as well as individual users, against cybersecurity threats. They also gather real-time threat intelligence data and perform security functions, such as deep packet inspection, to identify potential vulnerabilities.
Many small and medium-sized businesses use cloud-based UTM security products and services to handle security threat management with one system, rather than several smaller ones.
Who uses UTM systems?
Cybersecurity teams operating in a security operations center or similar facility are primary UTM users. Chief information security officers, chief technology officers and chief information officers use UTM system performance reports for insight on how well cyberthreats are being managed. Other C-level leaders might also use the reports, especially for situations that threaten company operations.
This article is part of
What is threat detection and response (TDR)? Complete guide
How UTM works
UTM solutions combine multiple security features into a single device or software program with a central management console. UTM products provide protection from primary threats, such as malware, phishing, social engineering, viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, hackers and denial of service (DoS). Understanding threats and identifying weaknesses to an organization's network are critical for security. A UTM system uses two inspection methods to do this:
- Flow-based inspection. Also known as stream-based inspection, flow-based inspection samples data that enters a network security device, such as a firewall or intrusion prevention system (IPS). The devices inspect the data for malicious activity, such as viruses, intrusions and other hacking attempts.
- Proxy-based inspection. This is a network security technique useful to examine the contents of packets that pass into and out of a network security device, such as a firewall, IPS or virtual private network (VPN) server. By using a proxy server to inspect these packets, the network security device can act as a proxy to reconstruct the content entering the device.
Pros and cons of UTM systems
UTM systems let cybersecurity teams address their key security diagnostic requirements in one system rather than use multiple tools. Properly configured, on-site or cloud-based UTM systems deliver a first line of defense against cyberattacks. They are flexible and adapt to various security scenarios, and organizations using them save money because they can eliminate multiple products and services.
Conversely, the principal attribute of UTM systems -- one system for all cybersecurity tasks -- also makes them a single point of failure. An on-site UTM system that uses a single central processing unit might get overloaded with too many concurrent activities and crash or suffer performance issues. Cloud-based UTM systems offer a way around this potential issue.
UTM devices
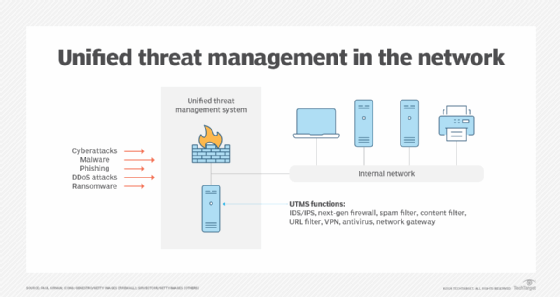
UTM devices are hardware or software that combine various network security features into a simple, easy-to-manage appliance. Besides having a firewall, VPN and IPS, UTM security appliances support network- or cloud-based centralized management. For example, Cisco Meraki appliances use a cloud-based management tool that can be deployed remotely on a per-device basis.
UTM features
UTMs typically include several security features and threat protection capabilities:
- Antispam service. This type of service, along with spam filters, scans inbound and outbound email traffic for signs of a possible attack and then blocks or tags incoming attacks. Algorithms scan message content for patterns associated with spam. Some systems look for certain words, others for specific language patterns and others for whole word patterns using Bayesian analysis. If the message appears to be spam or malware, the contents are tagged or quarantined.
- URL filtering and application control. UTM devices can perform URL filtering and application control. With application control, a UTM device puts specific applications on an allowlist so they connect to the internet without dealing with spam content filtering or other security measures. Application control is usually combined with a UTM device's firewall and other features to protect all traffic entering the corporate network.
- Firewall. A network firewall keeps unauthorized and malicious users from gaining access to data or resources, such as file servers, printers and web servers. There are three main types of firewalls: packet filtering, circuit-level gateway and application-level gateway.
- VPN. The VPN's role is to create a secure connection between two computers over a public network. This enables sharing files securely between co-workers, accessing data remotely or using any number of other services without fear that an outside party will intercept the data. VPNs use encryption to protect data from unauthorized access when crossing between public and private networks. They create a secure connection that is encrypted in a tunnel over the public internet.
- Content filtering. Web content filtering controls what information can pass into or out of a network, using various filtering methods, such as by IP address, port number or media access control address. Content filtering is used on networks to block unwanted content and provide data loss prevention functionality by filtering outgoing data to prevent transmission of sensitive information.
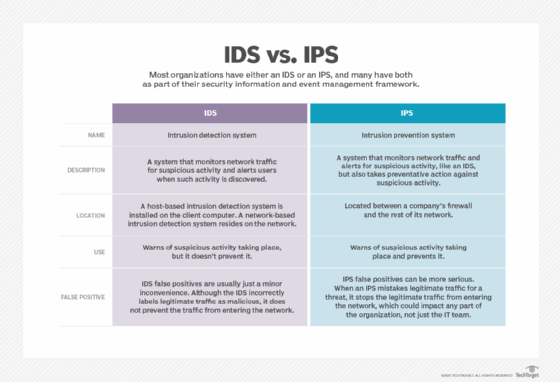
- IDS and IPS. An intrusion detection system monitors the network for signs of a cyberattack, while an IPS takes action to stop attacks and neutralize malicious traffic. An IDS seeks to detect abnormal behavior so it can be analyzed, recorded and reported. It can't block incoming threats, but can notify administrators about an intrusion and log the activity for later analysis. An IPS can be added to an existing IDS or firewall.
Tips for implementing a UTM system
When planning to install a UTM system, there are two key issues to consider before picking a UTM products or service to use and preparing a project plan:
- Understand cybersecurity management system requirements. Figure out what issues must be addressed. Are malware, phishing and distributed DoS incidents and attacks increasing? This may necessitate a different approach with greater protection. A change in how a company operates because of a merger, acquisition or downsizing could also require a shift in the amount of protection needed.
- Assess performance of existing systems. Take time to consider whether a change is necessary. If the current system or systems are on-site, would a cloud-based approach be better?
Firewall vs. UTM
UTM is a single system for cybersecurity threat detection, analysis and mitigation with a variety of specific security services. A firewall, on the other hand, protects network services and is typically the first point of contact for cyberthreats. Firewalls are hardware- or software-based security technology that monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and restrict access to a private network.
A next-generation firewall (NGFW) is a network security platform that provides a gateway between internal and external networks. A UTM system and NGFW serve similar purposes but differ in some key areas.
Originally developed to fill network security gaps left by traditional firewalls, NGFWs include application intelligence, an IPS and DoS protection.
Like an NGFW, a UTM system sits between external and internal networks and prevents cyberattacks from entering the internal network and its associated information systems. UTM systems typically include an NGFW, IDS, IPS, various filters, a VPN and other capabilities.
UTM refers to the ability of a single device to perform the functions of an NGFW, firewall and VPN. The major difference between these UTM systems and NGFWs is that a UTM system offers more features than an NGFW, such as an IPS and spam filtering, and is able to monitor and protect internal networks from intruders.
Future of UTM
With cyberattacks unlikely to decline in frequency or impact, UTM systems and other cybersecurity technologies will continue to be needed. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration will enhance UTM system performance and capabilities. Many vendors and service providers have already added AI to their products and services.
Learn more about protecting IT systems from all kinds of attacks in our in-depth cybersecurity planning guide.






