extranet
What is an extranet?
An extranet is a private network that enterprises use to provide trusted third parties -- such as suppliers, vendors, partners, customers and other businesses -- secure, controlled access to business information or operations.
Extranets, which take the form of external-facing websites or platforms, can sometimes be viewed as part of or an extension of the organization's intranet. This is because the information hosted on an extranet is typically only accessible on internal networks. Although information on an extranet is accessible to users outside the company, access is tightly controlled and only awarded to authorized users.
Some use cases for extranets include the following examples:
- exchanging large volumes of data using electronic data interchange;
- sharing product catalogs exclusively with wholesalers;
- collaborating with other companies on joint development projects;
- jointly developing and using training programs with other companies;
- providing services to a group of other companies, such as an online banking application managed by one company on behalf of affiliated banks; and
- sharing news of common interest exclusively with partner companies.
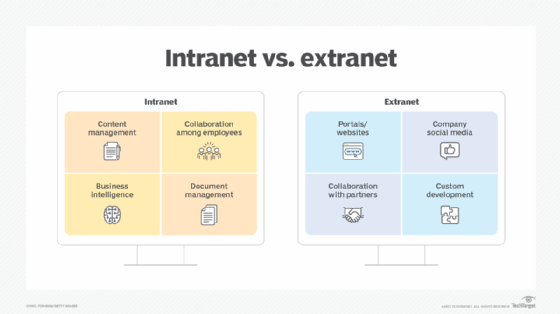
What is the difference between an intranet and extranet?
An intranet is a company's private network that hosts an internal website with various resources -- such as a knowledge base, communications channel and/or collaboration platform -- for employees and other select internal users, such as contractors.
Intranets help enhance efficiency and productivity by combining the features of blogs, document and content management systems, databases and wikis. Depending on the platform, they may also facilitate greater employee engagement through interactive features, such as commenting, chat, polls and more.
The primary difference between an intranet and extranet is that the intranet is a private domain. It can play a role in shaping company culture and internal communications, while also serving as a centralized repository for static resources, such as forms, policies and other employee tools. On the other hand, an extranet has a wider audience and a narrower objective, serving primarily as a platform to communicate information with important internal and external stakeholders who require access to internal information.
Sometimes, business intelligence applications also enable the placement of data visualization tools on the extranet to make essential data easily accessible to external stakeholders.
Both intranets and extranets require security and privacy. Whereas intranets can be accessed by users directly on the enterprise network, extranets -- by nature of being intended for third parties -- typically require some kind of virtual private network (VPN) connection or can be accessed via the internet with additional authentication measures.
Other security features can include firewalls, the issuance and use of digital certificates, and encryption.
What are the advantages of using an extranet?
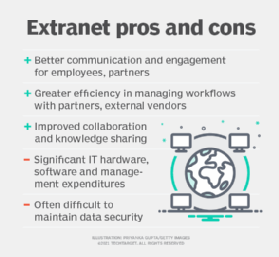
Extranets offer significant benefits for enterprises, employees and external partners:
- Enhanced engagement and communication. Extranets provide a platform for communicating important updates, making announcements or sharing important news relevant to all stakeholders. This approach can lead to increased participation and engagement from employees and external partners.
- Enhanced efficiency. Businesses of all sizes, including startups, often work with multiple partners and external vendors to develop products and complete tasks. An extranet helps manage these workflows.
- Enhanced collaboration and knowledge sharing. Before the emergence of popular team collaboration tools, like Asana, Trello and Jira, companies mostly depended on extranets and intranets to improve collaboration. This approach ensured seamless document sharing and real-time updates, while providing a secure environment to work with sensitive company data or project data.
What are the disadvantages of using an extranet?
Extranets also come with some drawbacks:
- Capital expenditure. Setting up and maintaining an extranet can be resource-intensive. The price includes the cost of on-premises hardware and software, as well as the costs associated with hiring information technology staff who must build it and maintain it. As a result, an extranet may not the best option for companies that do not have the financial resources to set up and manage it. Alternatively, managed or cloud-hosted extranets, such as Microsoft SharePoint, can help mitigate some of these upfront expenses.
- Data security. Using an extranet requires steps to mitigate risk. If security measures are lax, unauthorized users can potentially get in and access sensitive data. This may lead to the loss of proprietary or confidential data and competitive advantage. As such, extranets are best managed by in-house professionals who can help mitigate the risk of data leaks.
What is an extranet lockout?
Extranet lockout enables security teams to protect users from brute-force attacks when a threat is detected. In this scenario, Active Directory Federation Services, for example, can lock out malicious users from the extranet. Administrators can retrieve lockout event details from the security audit log.








