What is the dark web (darknet)?
The dark web is an encrypted portion of the internet not visible to the general public via a traditional search engine such as Google. Also known as the darknet, the dark web constitutes a large part of illegal activity on the internet. To a lesser extent, it is also used for lawful reasons by legitimate users such as those who want to protect the privacy of certain information or people looking to join an exclusive online club or social network.
What is the difference between the dark web vs. the deep web?
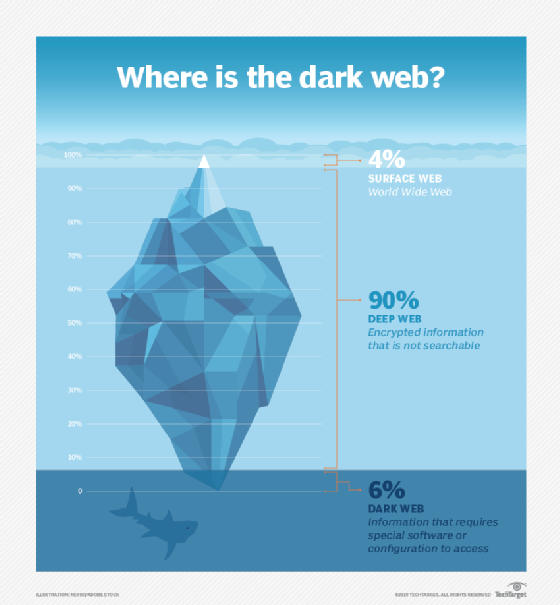
The dark web is a small, less accessible part of the deep web. Both share one thing in common: Neither can be found in search engine results. The main difference between them is in how their content is accessed. Deep web pages can be accessed by anyone with a standard web browser who knows the URL. In contrast, dark web pages require special software and knowledge of where to find the content.
How is the dark web accessed?
Indexes of website links allow Google and other search engines to return relevant results whenever a user types a keyword into the search bar. Websites on the dark web are not indexed by search engines. Instead, the dark web uses information from individual email or social media accounts, databases, and documents to give users access.
In addition, the dark web can't be accessed through typical browsers such as Firefox or Chrome. It can only be accessed through an encrypted peer-to-peer network connection or by using an overlay network, such as the Tor browser. Tor, short for The Onion Router, ensures complete anonymity on the dark web by using multiple encryption layers, a network of relays and a traffic-routing mechanism that randomly bounces internet traffic through these relays, rendering an IP address untraceable. The browser is free to download and use, and works with all major operating systems. In addition to the Tor browser, users can further protect their identities when accessing the dark web by doing so through a virtual private network (VPN).
Website URLs on the dark web
To access sites on the dark web, users must first know the URL for the site of interest. This is because these sites have an unconventional naming structure. Instead of common suffixes such as .com, .org and .edu, dark web URLs typically end in .onion, a special-use domain suffix associated with The Onion Router. Dark web URLs also contain a mix of letters and numbers, making them hard to find or remember.
Who uses the dark web?
The dark web's anonymity accommodates illegal activity and contributes to its reputation as being a haven for criminals. This anonymity, coupled with access difficulties and a high barrier to entry, facilitates all manner of illicit activities such as drug and human trafficking, weapons deals, and money laundering.
The dark web is used by those looking to buy or sell the following:
- Stolen credit card numbers.
- Stolen personally identifiable information.
- Stolen subscription credentials to streaming sites such as Netflix.
- Illegal content such as child sexual abuse material.
- Counterfeit money.
- Hacked enterprise accounts.
- Software and services to perpetrate cybercrimes such as ransomware attacks or phishing scams.
Often, dark web visitors use cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin to engage in such e-commerce transactions anonymously with reduced risk of being caught.
Despite its many shadowy uses, the dark web itself is not illegal, and it supports several legitimate uses. For example, it can help users communicate in environments or geographical areas where free speech isn't protected. Examples of such users include political activists and journalists. Legal dark web social media networks and clubs also exist. The dark web also hosts a large amount of content that cannot be found in any other part of the internet, such as banned books and "underground" discussion forums. And it supports the privacy needs of users for certain legal activities such as the exchange of proprietary business information.
Law enforcement agencies and cyber threat intelligence specialists also use the dark web. These professionals typically search it for information about cyberattacks, data breaches, scams and other illegal activities to better understand the threat landscape and design strategies to protect organizations, governments and the public from these threats.
Is the dark web dangerous?
Ironically, the Tor network surfaced in 2006 from a legal project jointly funded by the U.S. Navy and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or DARPA. It was largely the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009 that transformed the dark web into a sanctuary for criminals. Bitcoin also contributed to the emergence in 2011 of the Silk Road, a black market for buying and selling illegal drugs. The FBI shut down the Silk Road two years later.
Since the dark web is a hotbed of criminal and illegal activity, accessing it and using the content, tools or services found there can be extremely dangerous for both individuals and enterprises. Dangers of browsing the dark web include the following:
- Cyberattacks via viruses, ransomware, malware such as keyloggers, remote access Trojans or distributed denial-of-service attacks.
- Phishing.
- Identity theft.
- Credential theft.
- Compromise of personal, customer, financial or operational data.
- Leaks of intellectual property or trade secrets.
- Spying or cyberespionage.
- Webcam hijacking.
These dangers can interrupt business operations, defraud a company and devalue a brand's integrity. The best way to avoid these dangers is to avoid using the dark web entirely. But if this is not possible, it's important to employ reliable security measures, including antivirus software, and to access dark web sites only via a VPN. In addition, the Tor browser, Tor applications and operating systems should be kept up to date, and companies might want to limit or monitor their use.
For additional protection, enterprises should monitor the dark web to identify indicators of dark web compromise, such as database dumps or the posting of personal or financial information. Regular monitoring can provide early alerts of possible threats, which can facilitate prompt responses to mitigate the potential effects. Organizations can also consider dark web monitoring services that search through data available on the dark web for anything related to their specific company or employees. Dark web monitoring can supplement other tools used to gather preemptive threat intelligence, such as the Mitre ATT&CK framework.
Further explore why enterprise dark web monitoring is worth the investment.